Bleeding is a common clinical manifestation following trauma, while uncontrolled bleeding at the scene is identified as the primary cause of death. And absorbable hemostatic materials are useful as adjunctive therapy during surgical procedures when conventional methods, like ligation, do not control bleeding. Therefore, the significance of absorbable hemostatic materials in medical devices cannot be overstated. This article delves into the classification of these materials.
Absorbable gauze of oxidized regenerated cellulose refers to a specific type of gauze dressing that is made from oxidized regenerated cellulose fibers. The absorbable gauze is typically available in the form of a thin, woven or non-woven fabric that can be easily applied to wounds or surgical sites. Gauze Absorbable Hemostat is a medical gauze for surgery. Upon contact with blood or body fluids, the gauze absorbs the liquid, forming a gel-like substance. This supporting hemostatic device can be used instead of ordinary gauze during surgery, effectively stopping bleeding and reducing the possibility of postoperative adhesion. However, the oxidized regenerated cellulose gauze may have a slower absorption rate. In cases where rapid hemostasis is crucial, other materials with faster absorption rates may be preferred.
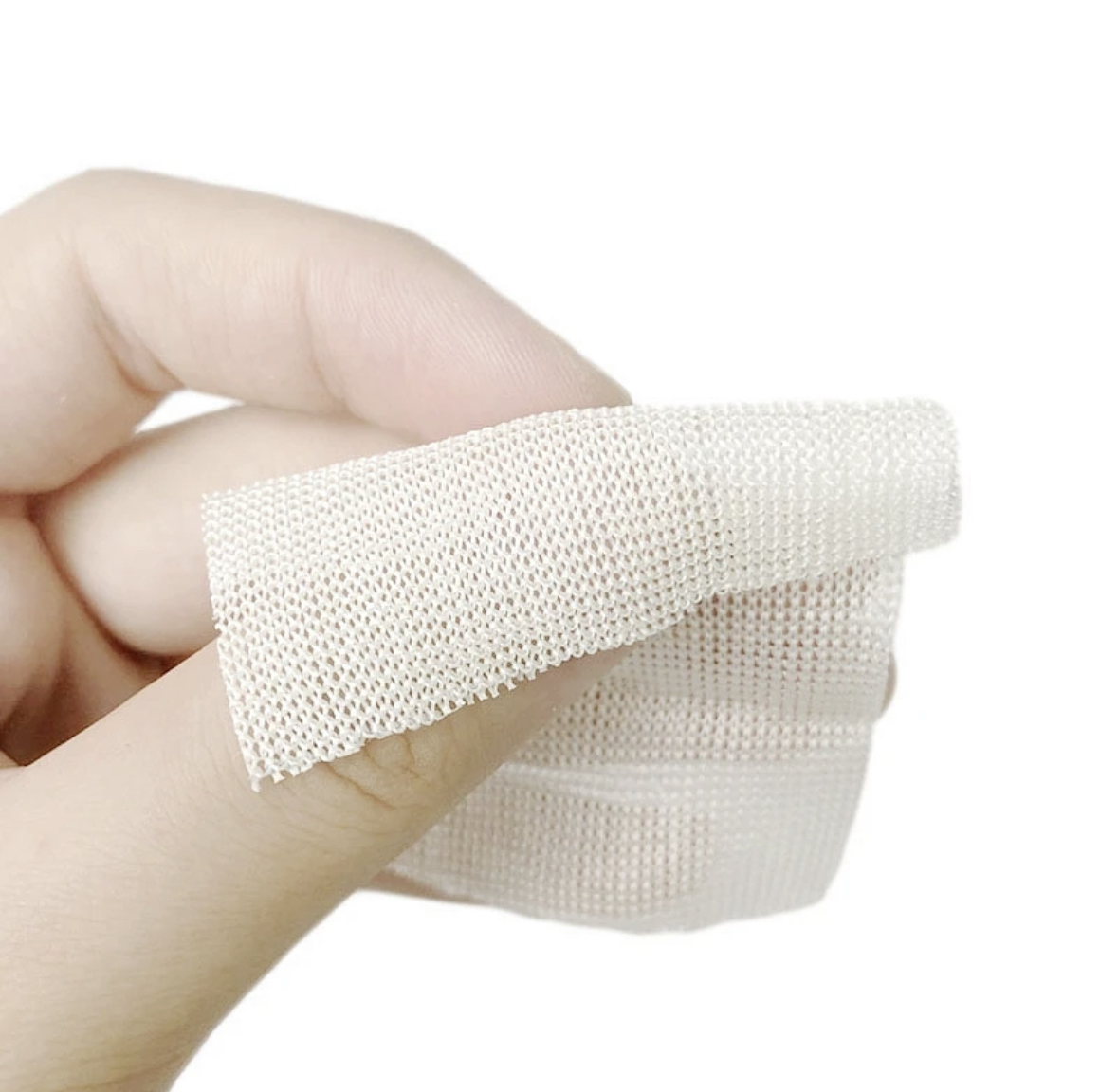

Fibril Absorbable Hemostat is a sterile, absorbable non-woven fabric prepared through the oxidation of regenerated cellulose. This process results in the non-woven fabric separating into layers and being molded to fit the wound or bleeding site, providing better coverage and contact with the affected area.

Hemostatic powder can be composed of modified starch, which can rapidly absorb moisture from the blood, causing the solid components such as clotting factors and platelets to aggregate on the surface of the particles, forming an "instant gel." This gel functions as a mechanical seal, blocking blood vessel openings and accelerating the endogenous clotting mechanism. Microporous Polysaccharide Hemospheres (MPH) Absorbable Hemostat utilizes potato starch as raw material through emulsification and crosslinking technology. These particles can absorb and lock water several times over their weight, forming gels with hydrophilic molecular sieve properties. The advantages of Powder Absorbable Hemostat is that it can apply for broad, irregular wound surfaces and Hard-to-Reach areas bleeding. However, hemostatic powder’s effectiveness might be limited in cases of large-area, deep bleeding. Additionally, prolonged use or certain circumstances may also trigger tissue inflammation reactions, necessitating guidance from healthcare professionals.
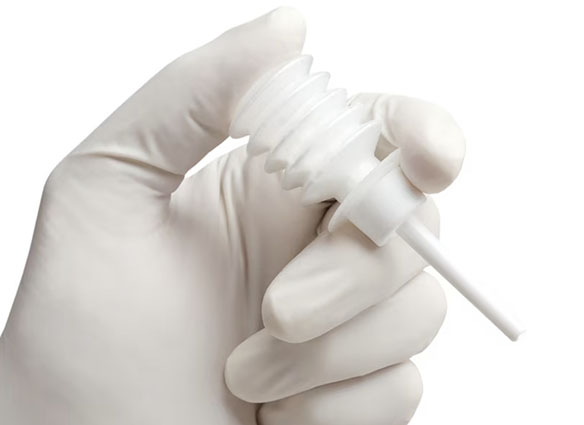
Gelatin, a hydrolyzed colloid used to promote the formation of fibrin, is available in various forms such as sponges, powder, and particles. The various formats of this material make it suitable for irregular wounds. This material can absorb up to 40 times its weight in blood and can expand to 200% of its initial size. With impressive absorbent capacity and room-temperature stability, gelatin exerts pressure upon application to achieve hemostasis. Notably, it also exhibits good biocompatibility, reducing the likelihood of allergic reactions. Gelatin-based hemostatic materials are rarely associated with feedback such as abscess or granuloma formation. However, these products pose safety concerns, as their characteristic "swelling" when used in confined spaces may lead to tissue damage. Consequently, they are not suitable for intravascular use.
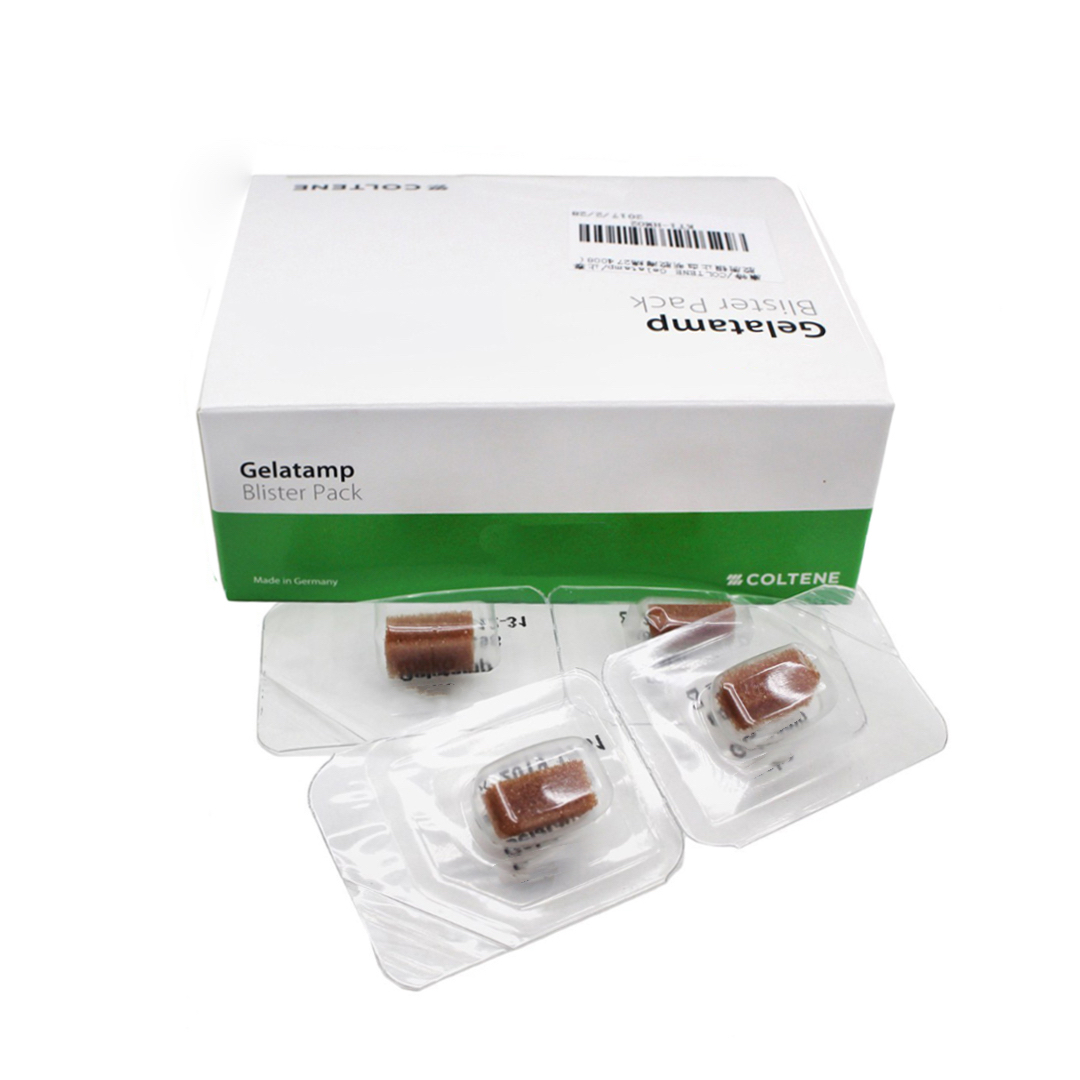
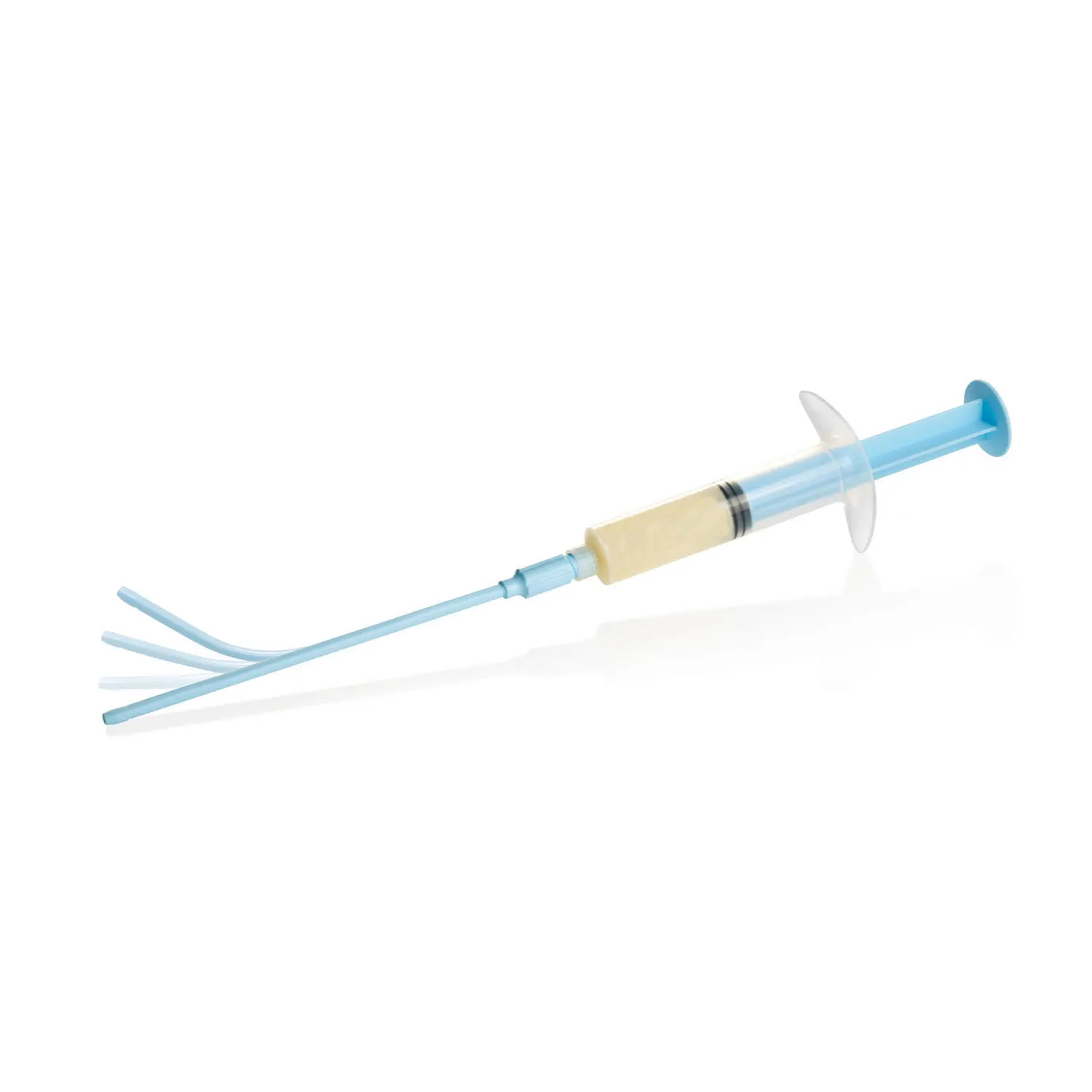
Thrombin's role in the hemostatic process involves accelerating the formation of fibrin in the blood, leading to the creation of a clot and consequently preventing bleeding. It is commonly formulated into absorbable products such as thrombin powder and thrombin gel to cater to various usage scenarios. These materials belong to a category of potent hemostatic agents, capable of rapidly inducing blood coagulation for swift hemostasis. Due to their high efficacy, the required dosage is typically minimal, reducing the burden on patients. However, it is important to note that some individuals may experience allergic reactions to thrombin, necessitating allergy testing prior to usage.
Each absorbable hemostatic material boasts unique advantages and disadvantages, necessitating careful consideration based on patient needs and clinical situations. In the ever-evolving landscape of medical technology, ongoing innovation and challenges in hemostatic materials continue to drive progress in medical science. By consistently optimizing the performance of hemostatic materials, we aspire to achieve more significant outcomes in medical practices. This aims to provide patients with safer and more effective treatment options.
-
singclean | 2023-11-17
 Mechanism of Delayed Redness and Swelling after Hyaluronic Acid Injection and Related Influencing FactorsIn recent years, hyaluronic acid injection has been favored in the field of medical beauty, but the problem of delayed redness and swelling after injection has also attracted widespread attention. Today, let's take a deeper look at the mechanism of delayed redness and swelling caused by hyaluronic acid injection and related influencing factors.
Mechanism of Delayed Redness and Swelling after Hyaluronic Acid Injection and Related Influencing FactorsIn recent years, hyaluronic acid injection has been favored in the field of medical beauty, but the problem of delayed redness and swelling after injection has also attracted widespread attention. Today, let's take a deeper look at the mechanism of delayed redness and swelling caused by hyaluronic acid injection and related influencing factors. -
singclean | 2023-11-17
 Tips For Lip Injection By Using Hyaluronic Acid
Tips For Lip Injection By Using Hyaluronic Acid -
singclean | 2023-11-17
 The Prevention and Treatment of OsteoarthritisOsteoarthritis is a chronic disease primarily caused by damage and wear and tear to joint cartilage, resulting in joint pain, stiffness, and limited function.
The Prevention and Treatment of OsteoarthritisOsteoarthritis is a chronic disease primarily caused by damage and wear and tear to joint cartilage, resulting in joint pain, stiffness, and limited function.




